Analog to digital converter without ADC
There are some low-cost systems that require reading from some sensors, potentiometers, or other analog devices, by using a cheap microcontroller without an integrated analog to digital converter.
Adding an external ADC might require more microcontroller pins, more space in the PCB, or more software complexity (for instance, I2C routines may be needed if that’s the used bus).
If there aren’t many requirements regarding resolution, accuracy, linearity, sample time, the solution is to use an RC circuit and measure the time it takes to charge (similar to a double ramp ADC)
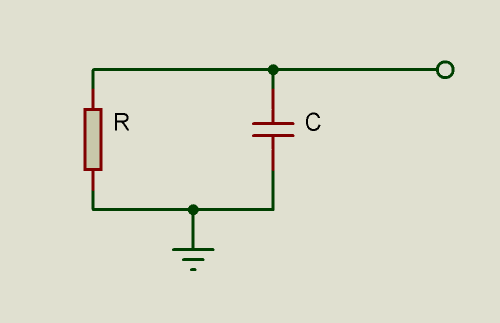
The resistor could be replaced with a thermistor (PTC or NTC) if the temperature of something has to be measured, or with an LDR to measure luminosity. It’s also possible to use this circuit to measure capacitance if the resistor value is fixed.
This circuit requires a bidirectional pin in the microcontroller, which should also allow setting a high impedance (High-Z) input state.
The principle is the following:
- Set the pin to high for around 1 millisecond to charge the capacitor
- Set the pin in a high-z state and measure how long the capacitor holds the charge.
- Repeat the cycle according to the desired sample rate.
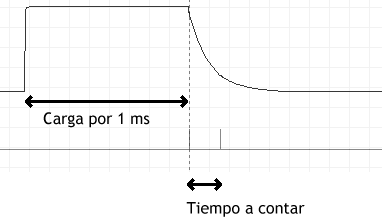
A small way to program it would be the following:
uint16_t time = 0;
DIR_LOAD = OUTPUT;
PIN_LOAD = 1; delay1ms(); PIN_LOAD = 0; // Charge the capacitor
DIR_LOAD = INPUT;
while(PIN_LOAD == 0) time++; // Wait for the capacitor to discharge and count the time
The 16 bit output should then be scaled to get a correct value according to the resistor. To avoid wasting CPU time in the while loop, an internal capture module may be used to easily count the interval during which the pin was in a high state. This method works best with pins that feature Schmitt Trigger capability, since it helps to remove the dependency of the supply voltage in the measured times.